Applies To:
Show Versions
BIG-IP LTM
- 14.1.2, 14.1.0
Configuring HTTP/2 Full-proxy Support on the BIG-IP System
Overview: HTTP/2 full-proxy configuration
When your application server infrastructure is composed of HTTP/2-enabled servers, you can take advantage of the HTTP/2 acceleration features that the BIG-IP system provides. Most importantly, the BIG-IP system includes full-proxy support for the HTTP/2 protocol. This means that the BIG-IP system can process HTTP/2 requests and responses on both the client and server sides of the BIG-IP system.
The HTTP/2 full-proxy architecture provides greater network efficiency by allowing the BIG-IP system to transport multiple simultaneous, bi-directional streams of messages between the client and server. This is accomplished through the use of the BIG-IP system’s message-routing proxy, instead of the traditional connection-oriented TCP proxy.
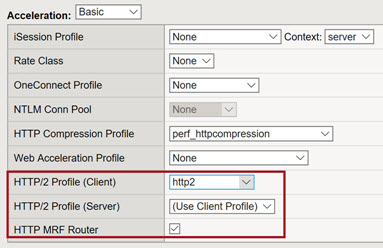
This figure shows an example of the Acceleration area of the New Virtual Server screen, where you configure some key settings for successful HTTP/2 full-proxy operation.
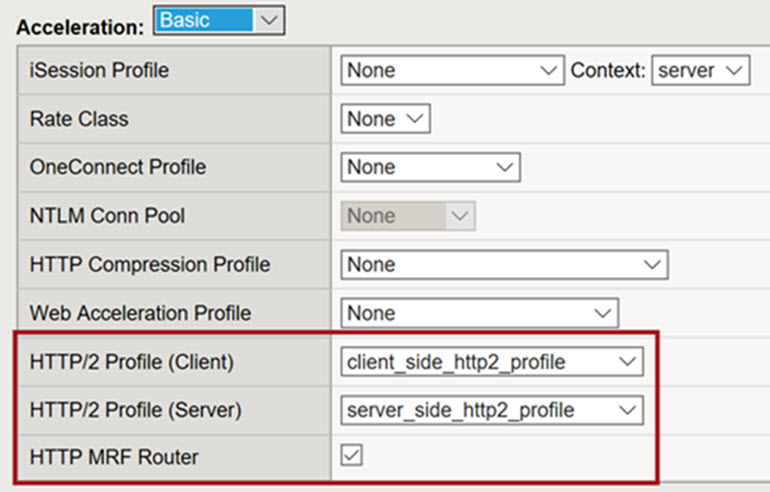
Configuration summary
To configure HTTP/2 full-proxy support on the BIG-IP system, you can use the BIG-IP Configuration utility.
This illustration shows the tasks required to deploy an HTTP/2 full-proxy configuration. Note that you do not need to create a custom Client SSL profile because when you create the virtual server, you will be assigning an existing profile named clientssl-secure to it.
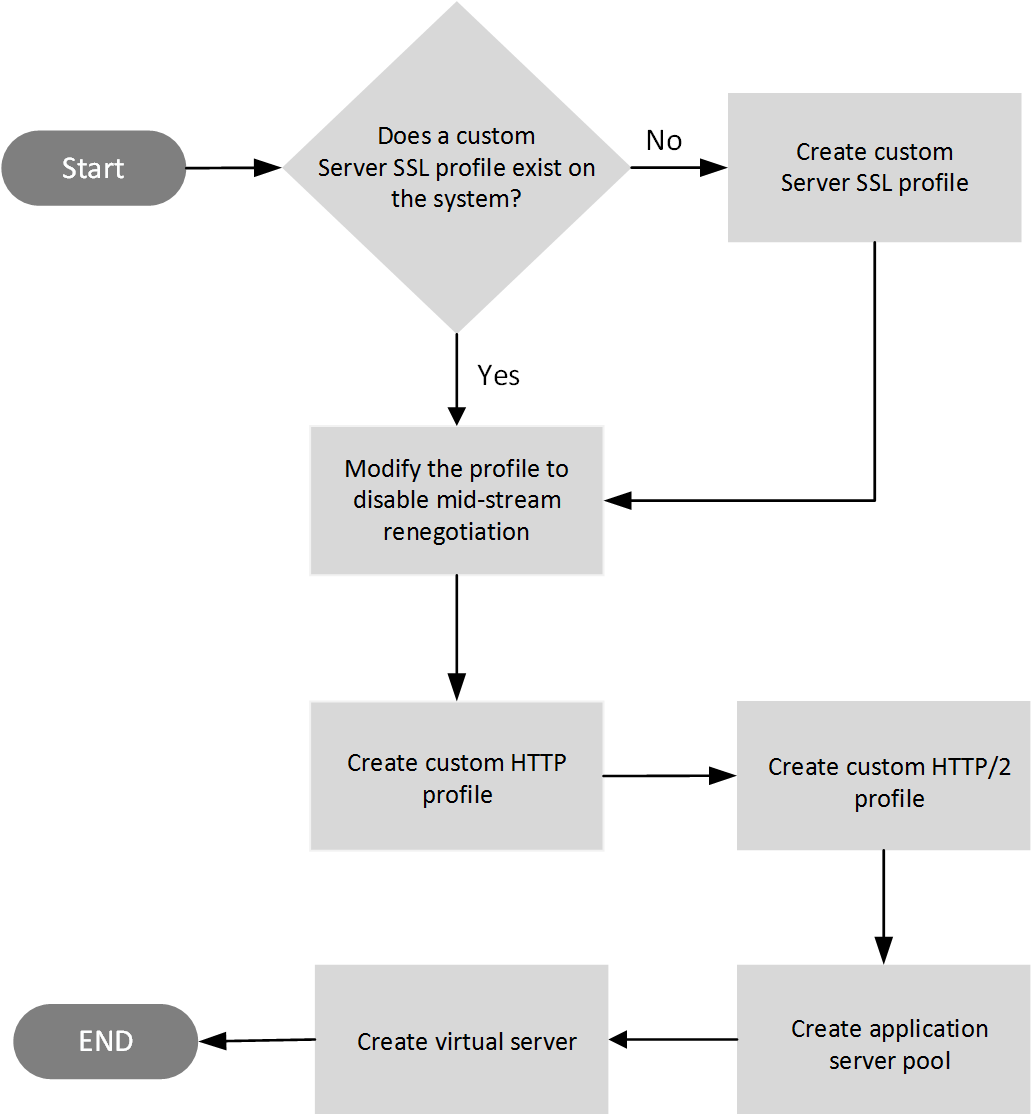
Configuration constraints
There are a few BIG-IP system constraints that you'll want to be aware of before deploying an HTTP/2 full-proxy configuration:
- An HTTP/2 full-proxy configuration works with BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager (LTM) only. The configuration is not supported on any optional BIG-IP modules.
- The OneConnect and HTTP Cache features are not supported.
- The HTTP/2 protocol is incompatible with NTLM protocols.
- For session persistence, only the Cookie persistence method is available.
- In high-availability configurations, connection mirroring is not supported.
- The iRule commands session and table are not supported.
- The Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is not supported in HTTP/2 environment. Do not attach both HTTP/2 profile and VDI profile together in the virtual server.
Disable server-side SSL renegotiation
- On the Main tab, click .
- In the Name column, click the name of the relevant Server SSL profile.
- From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
- For the Renegotiation setting, clear the check box.
- At the bottom of the screen, click Update.
Create a custom HTTP profile for HTTP/2 full-proxy configuration
Part of configuring an HTTP/2 full-proxy configuration on the BIG-IP system is to first create a standard HTTP profile. An HTTP profile defines the way that you want the BIG-IP system to manage HTTP traffic.
Create a custom HTTP/2 profile
Part of creating an HTTP/2 full-proxy configuration is to create an HTTP/2 profile that you can use for both client-side and server-side application traffic. When you assign the profile to a virtual server, the BIG-IP system applies the settings in the profile to the traffic.
Create a basic server pool to process HTTP/2 traffic
You can create a pool of application servers enabled for processing HTTP/2 traffic. After creating the server pool, you must assign the pool to a virtual server.
Create a virtual server to manage HTTP/2 traffic
You must create a virtual server to listen for HTTP/2 traffic, apply profiles and policies, and send the traffic to a pool of application servers that are HTTP/2-enabled.
View statistics for an HTTP/2 full-proxy deployment
You can view statistics for either client-side or server-side HTTP/2 traffic.